Resources
Categories
Molecular crowding affects induction of stem cell differentiation

What is molecular crowding (Macromolecular Crowding: MMC) ?
We guess for many people the term molecular crowding is not familiar. According to a search in PubMed, the number of papers published about it in 2017 is 63, making it seem not a hot topic of research yet. However, since Minton et al. published a paper on the influence of molecular crowding on the structure and function of enzymes in 1981, knowledge regarding it has steadily grown.
Molecular crowding refers to the nonspecific effect of steric repulsion between molecules in specific reactions and processes occurring in solutions in which large volumes are occupied. However, it is difficult to understand this concept by words, so the following figure gives an outline on what molecular crowding is. In a solution in which a polymer is present at a high concentration (crowded), small size molecules are accessible without being restricted from migration, but in the case of molecules of a large size the accessible area is limited. In addition, since molecular crowding significantly lowers the diffusion rate of molecules, steric interactions between molecules greatly influences the diffusion-controlled reaction (the reaction rate depends on the diffusion rate of the substance required for the reaction1). Furthermore, protein folding is also said to be affected by MMC.
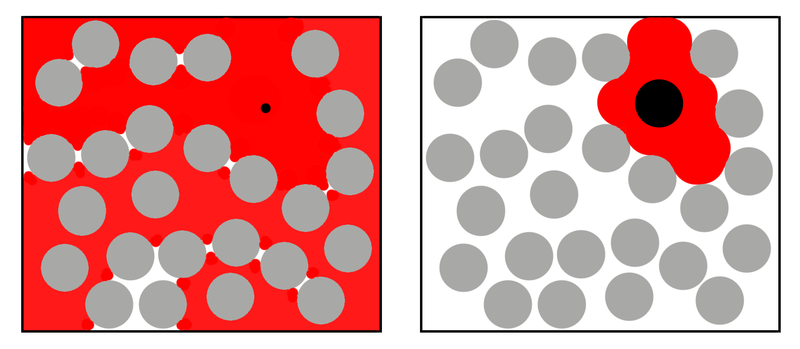
Molecular crowding in the life sciences
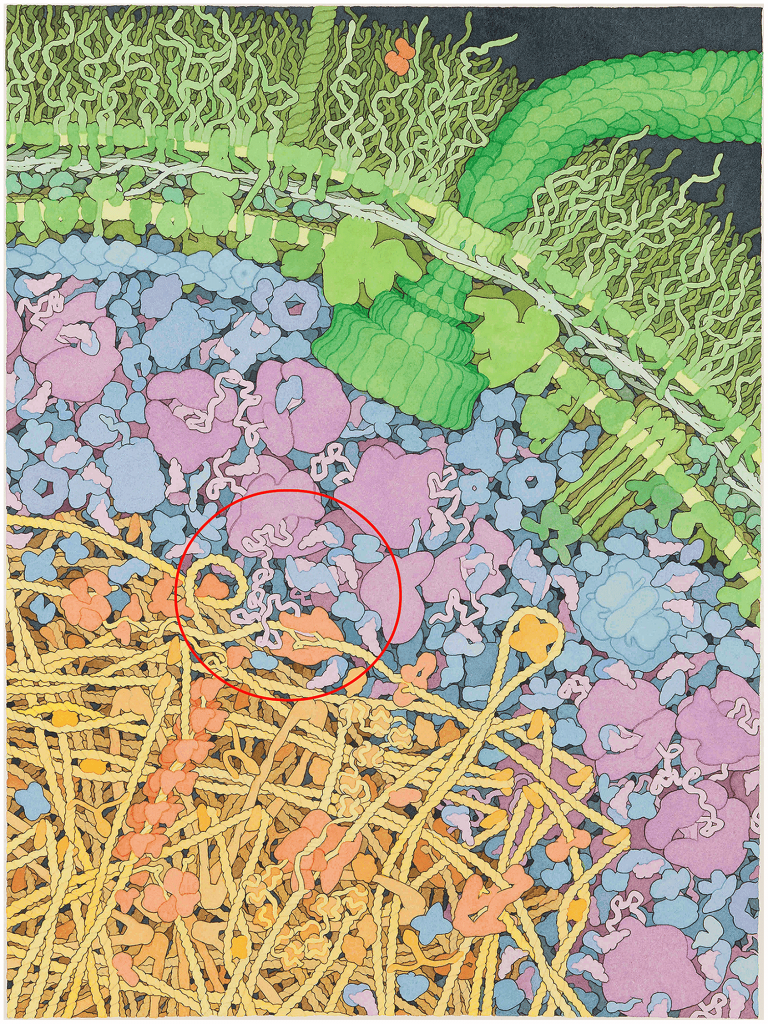
What is known about molecular crowding in the life sciences? Generally, in in vitro experiments it is said that macromolecules exist at concentrations of 1 g / L or less, while polymers are present at a concentration of several hundred g / L in in vivo. In addition, the proportion of macromolecules in cells to their volume is considered to be 10 to 40%, which is considered to be a rather crowded environment.
Therefore, in order to reproduce the crowded environment described above in in vitro experiments, researchers in the field of molecular crowding have been using inactive polymer crowding agents. Known crowding agents include albumin, dextran, Ficoll, polyethylene glycol and polystyrene sulfonic acid3).
Influence of molecular crowding on the living body
According to the Banerjee et al. and Shirai et al. papers published in 2016, molecular crowding promotes the formation of α-synuclein fibres, a major component of Lewy bodies that are characteristic of Parkinson’s disease, which helps to understand its disease progression. The effects of molecular crowding are extensive and include an increase in collagen deposition, acceleration of actin polymerisation and stabilisation of DNA supercoil structures.
In addition, as shown in the table below, molecular crowding has been applied in fields related to regenerative medicine, which has been actively studied in recent years, and it is also used for culturing stem cells and inducing their differentiation. For example, Lee et al. described that collagen gel is able to induce differentiation of brown adipocytes similar to the molecular crowding effect by Ficoll.
| Crowding agent | Outline | Article |
|---|---|---|
| Dextran | Extracellular matrix was obtained by culturing retinal pigment epithelial cells under MMC conditions, which was then used for promoting induced pluripotent stem (iPS) cells to differentiate into retinal pigment epithelial cells. | McLenachan S, et al. Biochem Biophys Rep. 2017 Mar 28;10:178-185. |
| carrageenan, Ficoll |
Bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells (BM-MSCs) were cultured using MMC conditions and induced to differentiate into adipocytes, osteocytes and chondrocytes. | Cigognini D, et al. Sci Rep. 2016 Aug 1;6:30746. |
| Ficoll | BM-MSCs were induced to differentiate into white and brown adipocytes under MMC conditions (collagen gel was also used). | Lee MH, et al. Sci Rep. 2016 Feb 17;6:21173. |
| Ficoll | Peripheral blood mononuclear cells were cultured under MMC conditions and MSC-like pericytes were obtained. | Blocki A, et al. Mol Ther. 2015 Mar;23(3):510-22. |
| Ficoll | BM-MSCs were induced to differentiate into adipocytes. | Ang XM, et al. Tissue Eng Part A. 2014 Mar;20(5-6):966-81. |
| Dextran, Ficoll |
Extracellular matrix was obtained by culturing fibroblasts under MMC conditions, which was then used for culture of ES cells. | Peng Y, et al. J Tissue Eng Regen Med. 2012 Nov;6(10):e74-86. |
| Ficoll | BM-MSC were cultured under MMC conditions. | Zeiger AS, et al. PLoS One. 2012;7(5):e37904. |
| Ficoll | BM-MSCs were induced to differentiate into adipocytes and osteocytes under MMC conditions. | Chen C, et al. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2011 Apr 30;63(4-5):277-90. |
Reference
1) Life in a crowded world.
Rivas G, Ferrone F, Herzfeld J.
EMBO Rep. 2004 Jan;5(1):23-7. PMID: 14710181.
2) Easy DNA modeling and more with GraphiteLifeExplorer.
Hornus S, Lévy B, Larivière D, Fourmentin E.
PLoS One. 2013;8(1):e53609. PMID: 23308263
3) Making microenvironments: A look into incorporating macromolecular crowding into in vitro experiments, to generate biomimetic microenvironments which are capable of directing cell function for tissue engineering applications.
Benny P and Raghunath M.
J Tissue Eng. 2017 Oct 6;8:2041731417730467. PMID: 29051808.