Topics
-
- Newsletters22/07/2025Challenging mass culture of mesenchymal stem cells: Soluble microcarriers
- Newsletters23/06/2025A Three-Minute Guide: Applications of the ubiquitous collagen solution
- Newsletters12/05/2025Two skin models: Accelerated maturation of the epidermal model and a contraction-suppressed full-thickness skin model
- Newsletters15/04/2025Coating only? Four key applications you should know ー Various uses of Atelocollagen ー
- Newsletters11/03/2025Three techniques for cell transplantation -what are the benefits? Precautions are also shown.
- Newsletters14/02/2025Aiming for human induced pluripotent stem cell (iPSC) production for clinical use -3D culture with atelocollagen-
- Newsletters18/11/2024Overcoming the limits of in vivo evaluation with high efficiency of over 70%-A webinar on in vivo evaluation presented by three experts-
- Newsletters18/10/2024Ten selections from substances used in combination with atelocollagen ー New research seeds ー
- Newsletters09/09/2024Seven types of collagen, seven papers ー Applications in cancer research ー
- Newsletters22/08/2024Reducing the culture time by half ーAccelerated maturation of epidermal modelsー
What is Atelocollagen?
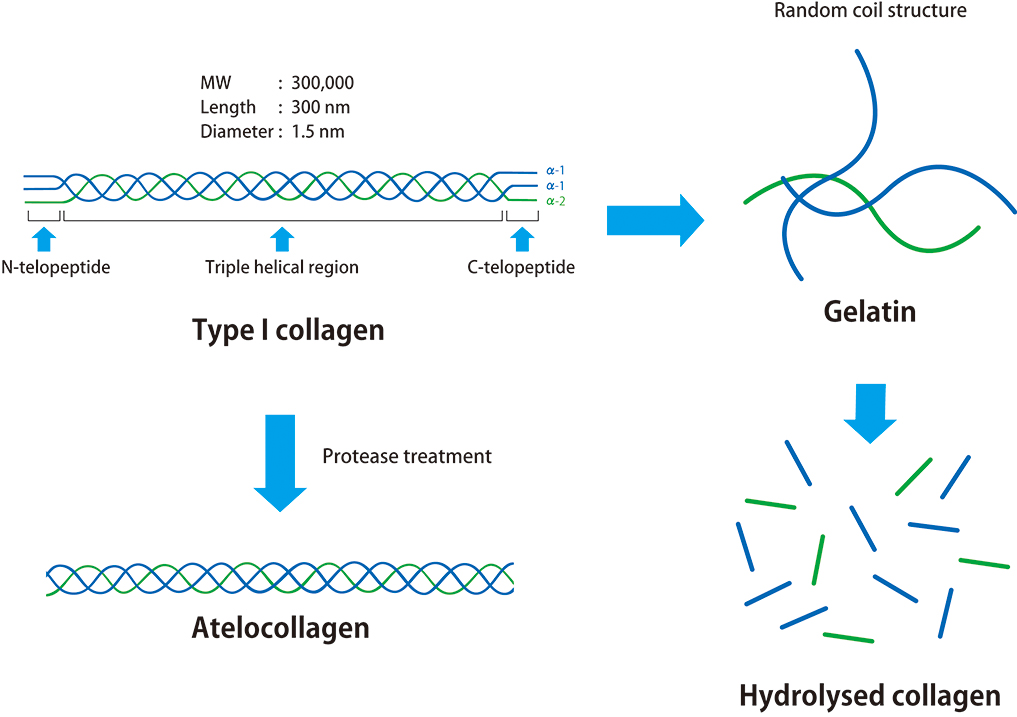
Collagen is an extracellular matrix found in the dermis, ligaments, bones, etc., and accounts for approximately 30% of the total protein in the human body. The most abundant type of collagen is type I collagen, which has a molecular weight of approximately 300 kDa and comprises three polypeptides. The molecular structure of collagen is a right-handed triple helix region and telopeptide (non-helical) regions at the N-terminal and C-terminal of the molecule. These telopeptide regions are composed of two α1 chains and one α2 chain. The triple helix region is conserved among species and shows low immunogenicity, while the telopeptide regions exhibit high immunogenicity. Removal of the telopeptide regions by protease treatment produces atelocollagen, which retains the same properties as collagen. We have developed atelocollagen-based medical devices.
Unwinding of the triple helix of collagen and atelocollagen by heat degeneration produces gelatine. Gelatine is a random coil single polypeptide and has high immunogenicity.Peptides obtained by hydrolysis with strong acids, strong alkalis, or by enzymatic treatment are called hydrolysed collagen. Gelatine and hydrolysed collagen have totally different properties from collagen due to their structural differences compared to collagen.