Show Q&A menu
- 3D Ready Atelocollagen
- Collagen Acidic Solutions/Neutral Solutions
- 3D Honeycomb Boosted
- Atelocollagen, Honeycomb Sponge
- Atelocollagen Sponge, MIGHTY
- Atelocollagen Coated β-TCP Scaffold
- Atelocollagen Microspheres
- Collagen Sponge for 35 mm Culture Dish
- FibColl® Atelocollagen Inserts 24
- Atelocollagen, Permeable Membrane
- Type II Collagen
- Atelocollagen Powder, Membrane, Sponge
- Others
Collagen Acidic Solutions/Neutral Solutions
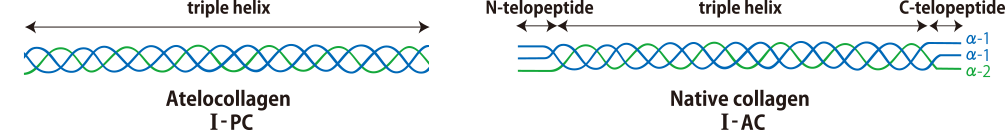
What are the differences between I-PC and I-AC?
I-PC is protease solubilised atelocollagen whose immunogenicity is reduced while maintaining the functions of collagen. I-PC is suitable both for gel formation and for collagen coating because of its relatively low viscosity. On the other hand, I-AC is acid-soluble collagen which retains telopeptides. Its viscosity, transparency and rigidity are higher than those of I-PC.
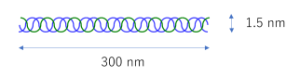
What is the size of the collagen molecule?
The size is approximately 300 nm in length and 1.5 nm in width, and the molecular weight is approximately 300,000.
Collagen is composed of three molecular chains that form a triple helical structure.
The molecular chain is a polypeptide consisting of approximately 1000 amino acids bound together in a unique amino acid sequence of collagen repeating [Gly-X-Y].
Phenylalanine, histidine, proline, glutamic acid, and leucine are primarily in the X position, whereas hydroxyproline and hydroxylysine are typically found in the Y position.
What is atelocollagen?
Telopeptide is a non-helical structure at both ends of the collagen molecule and is thought to be involved in intermolecular bonding and allergenic reaction due to antigenicity. Removing the telopeptides from collagen by protease treatment produces atelocollagen whose characteristics are superior purity and stability. We have produced atelocollagen-based medical devices for more than 30 years.
What types of collagen are contained in Collagen acidic solutions and Collagen neutral solutions?
The source of collagen is bovine dermis and therefore both products contain approximately 95% type I collagen and roughly 5% type III and type V collagen.
What is the difference between collagen acidic solutions and collagen neutral solutions?
Collagen is highly stable in acidic conditions and is appropriate for long-term storage. In contrast, collagen forms a gel under physiological conditions and thus must be neutralized and mixed with medium. This is why we have prepared Collagen neutral solution and 3D ready atelocollagen which readily form a gel upon warming. The collagen contained in Collagen neutral solution and 3D ready atelocollagen are atelocollagen.
Under what solvent conditions does collagen form a gel?
Collagen molecules form fibers with the same period (670Å) as natural fibers when warmed to 37°C in a neutral solution like phosphate-buffered saline with a salt concentration of 0.9% NaCl and pH around 7.4, forming a gel.
How can I prepare collagen coatings/collagen gels?
Please visit our distributors’ page to download an instruction manual
Why mix the medium (10x concentration) as indicated in "Preparation of collagen gel medium" from the manual?
Sodium chloride and other substances included in the concentrated medium are required for collagen to gel. Although 10x medium is indicated in the manual to maximize the final collagen concentration, any concentrated medium can be used if the medium is diluted to 1x final concentration. The concentrated medium can be prepared by dissolving commercially available powder-type medium to any desired concentration. If you wish to prepare collagen gels without additional medium components, concentrated PBS can be substituted.
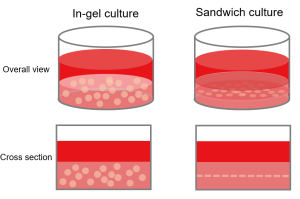
Can cells cultured on a gel with atelocollagen be observed?
Because each cell is at a different height in the gel, the microscope cannot focus on every cell; however, the morphology of individual cells can be observed.
If you want to culture cells at a certain height, consider sandwich culture in which a collagen gel without cells is formed first, cells are seeded on top of the collagen gel, and then another layer of collagen gel is added.
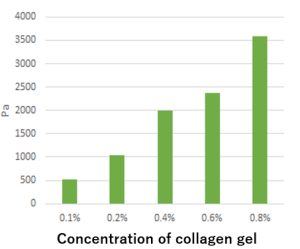
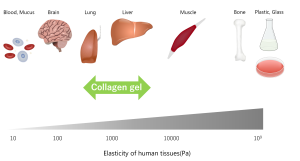
How strong is the atelocollagen gel?
The graph below shows a representative measurement of compressive strength.
Plastic petri dishes and plates for culture are much stronger compared to tissues.
On the other hand, the strength of the atelocollagen gel is closer to that of native tissue and decreases at lower collagen concentrations.
If you are interested, please also see the video about the collagen gels.
Source of illustration: ©2016 DBCLS TogoTV / CC-BY-4.0
Have collagen solutions been used to culture iPSCs?
Collagen coating has been used to culture iPSCs, and collagen gels have been used as skin transplants using iPS cell-derived keratinocytes.
How can collagen be used to create in vitro skin models?
Skin models have been created by culturing fibroblasts in a collagen gel and then adding keratinocytes. Native collagen is more often used than atelocollagen because of the relatively low shrinkage of collagen gel by fibroblasts.

How can I prevent cells from sinking during collagen gel formation?
When a low concentration of collagen is used, the viscosity is low and the gelling time is longer. We recommend using 5 mg/mL Atelocollagen or Native collagen acidic solution (Cat No. IPC-50 or IAC-50) or 3D Ready Atelocollagen (Cat No. 3D-LG01 or 3D-HG01).
How can I harvest cells from collagen gel?
Add collagenase to final concentration of 0.1% and incubate at 37°C for approximately an hour.
Is it possible to prepare sections from collagen gel?
Similar to tissue samples, collagen gel can be fixed and/or embedded in paraffin/OCT compound.
How can I analyze protein expression in cells cultured on collagen gel using western blotting?
The extract obtained by lysing the cells together with the gel using lysis buffer can be analyzed by western blotting as is. If the protein of interest cannot be detected, the collagen gel should be lysed in advance using collagenase*.
*Commercially available collagenase for cell dispersion contains a wide variety of proteases; therefore, ensure that the collagenase you use does not contain an enzyme that degrades the target protein.
Is there a high concentration collagen solution that is ideal for cell transplantation?
We can provide a collagen solution equivalent to that used in manufacturing our atelocollagen-based medical devices as a made-to-order research product. Alternatively, a high concentration collagen solution can be prepared from Atelocollagen powder (Cat No. CLP-01).
What are the differences between soluble basement membrane extracts and collagen solution?
Our collagen solution does not contain cell-derived physiologically active compounds, nucleic acids, matrix metalloproteinase (MMP), etc., which could affect the results of your experiment. Unlike soluble basement membrane extracts, we confirm the lot-to-lot consistency of our collagen products.
Information on this page is based on published articles and in-house data.